What is the Difference Between UHMWPE and HDPE?
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and UHMW (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) are both thermoplastic polymers made from ethylene monomers. At a glance, they can look quite similar. Both materials start with the same basic ingredients—ethylene and hydrogen gas. The difference lies in the type of catalyst used during polymerization. HDPE is produced using a Ziegler-Natta catalyst, while UHMW relies on a metallocene catalyst.
HDPE is versatile and can be molded using injection or blow molding techniques. It can also be formed into sheets that are later shaped through thermoforming, vacuum forming, or plastic welding. It’s a go-to material for making chemical containers and water tanks thanks to its strength and chemical resistance.
UHMW, on the other hand, is an extremely durable and cost-effective material known for its outstanding wear resistance. It’s widely used in high-abrasion environments.

What is UHMW?
Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, commonly known as UHMW or UHMWPE, is a member of the thermoplastic polymer family. What sets UHMW apart is its extremely high molecular weight—typically between 5 and 9 million atomic mass units (AMU). This comes from its exceptionally long polymer chains, all of which are aligned in the same direction. These chains are tightly bonded to one another through Van der Waals forces, which makes them harder to separate. As a result, UHMW has outstanding toughness and impact resistance.
Like HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), UHMW is also made by polymerizing ethylene. However, the difference in polymerization processes leads to UHMW having a higher molecular density and enhanced performance in specific areas.
What is HDPE?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a type of thermoplastic polymer. Compared to other forms of polyethylene, HDPE has a higher density—around 0.95 g/cm³. This is due to its low degree of branching, which allows the polymer chains to pack closely together. As a result, HDPE is tougher and has better impact resistance. Even when exposed to temperatures up to 120°C, its performance remains stable, making it suitable for high-pressure steam sterilization.
HDPE vs. UHMW: Applications and Uses
Thanks to their excellent performance characteristics, both HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and UHMW (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) are widely used across a variety of industries. In some cases, the two materials overlap in application, while in others, one is clearly the better choice due to its unique properties.
Shared Applications of HDPE and UHMW
Both materials are used in settings that require durability, chemical resistance, and ease of cleaning. Common overlapping uses include:
Food and beverage processing and storage equipment
Kitchen fixtures: cabinets, countertops, and worktables
Unique Applications of UHMW
UHMW stands out for its extreme durability, light weight, and excellent chemical and corrosion resistance. It's ideal for high-wear and mechanical parts. Exclusive applications include:
Assembly line components
Wear strips, bushings, star wheels, guide rails, and conveyor parts
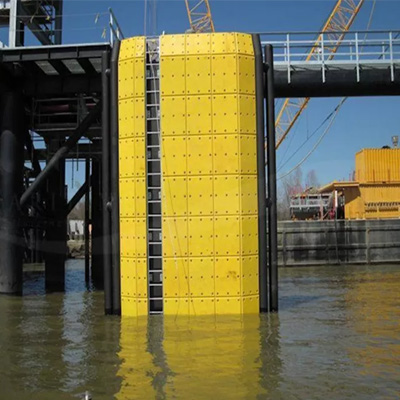
Dock bumpers and marine fender systems
Bulletproof vests and protective gear
Electrical components

Unique Applications of HDPE
HDPE is highly valued for its durability and weather resistance. It’s resistant to insects, mold, and rot, and it’s easy to shape and mold into nearly any form. These features make HDPE ideal for long-term outdoor use and a wide range of other products, such as:
Patio furniture
Playground equipment
Storage containers
Recycling bins and trash cans
Compost bins
Plastic lumber
Vehicle components
HDPE is also a popular material in kitchens. It’s commonly used in cutting boards, cabinetry, countertops, worktables, small kitchen appliances, and various food and beverage containers.
HDPE vs. UHMW: Physical Properties
Both HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and UHMW (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene) offer impressive physical properties that make them suitable for demanding applications. The table below compares some key characteristics of these two materials:
| Property | HDPE | UHMW |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point (°C) | 118–137 | 133 |
| Density (g/cm³) | 0.93–0.97 | 0.93–0.95 |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 50–76 | >63 |
| Tensile Yield Strength (MPa) | 11–43 | 20 |
| Tensile Elongation (@ 73°F, %) | 600 | 350 |
| Water Absorption (%) | 0.010–0.10 | 0.010 |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Good |
| Heat Deflection Temp @ 0.46 MPa (°C) | 42.8–93.3 | 65 |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Good |
Environmental Considerations
Recyclability and Eco-Friendliness
Both materials are recyclable, but HDPE has a more established recycling stream. UHMWPE is often reused in industrial settings but isn't as commonly recycled through curbside programs.
Lifespan and Durability
UHMWPE lasts longer in rugged environments. HDPE, while durable, can degrade under constant UV exposure without stabilizers.
Industry Perspectives and Standards
Compliance and Certifications
HDPE is FDA-approved for food contact.
UHMWPE also meets FDA and USDA guidelines, particularly in medical and food-grade uses.
Trusted Suppliers and Manufacturing Best Practices
When sourcing, go with certified manufacturers that follow ASTM and ISO standards. This ensures you're getting material with consistent properties and performance.